4 Other Types of Machine Learning
Generating predictions by learning from input/output pairs only refers to a part of the discipline of Machine Learning, also known as supervised learning.
It is called “supervised” because the algorithm learns from labelled examples. As an example, a model learns to predict the diagnosis of a suspicious mass from its measurements.
Supervised learning will be the main focus of this book. This section will briefly explore other types of Machine Learning.
Sometimes, these labels do not exist. Let’s imagine an archaeologist who stumbles upon a pile of bones. They want to understand if all the bones belong to the same species. One possible approach would be to measure all of these bones. In a simplified case, there are two measurements, length and width.
Plotting all these bone measurements on a chart, two clusters emerge:
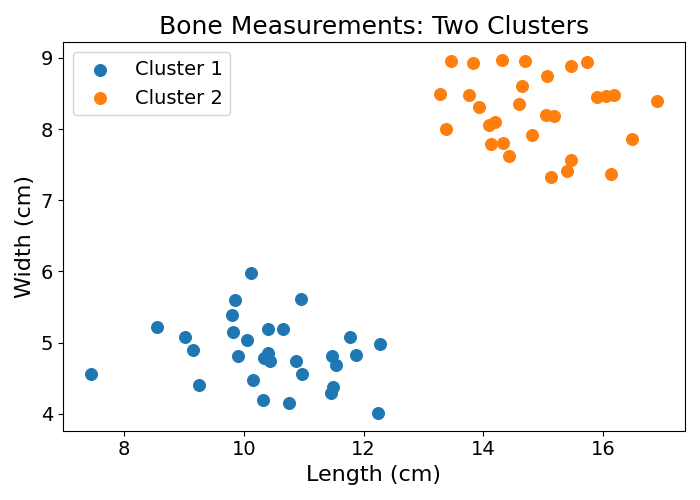
The exact species are still unknown, but the bones seem to belong to two different clusters. You have gained this information through the use of unsupervised learning, learning patterns or underlying structures of the data.
Exercise 4.1 Could a similar approach be used to discover the different customer groups of an online business? What data would you collect? And what would you do with it?
4.0.1 Reinforcement Learning
Another type of Machine Learning is reinforcement learning (RL), in which the Machine Learning algorithm does not generate predictions, but selects actions to maximise a certain reward within an environment. As an example, the objective of a RL algorithm could be to win at chess. At each move:
- the algorithm chooses an action: the next move
- based on its environment: the current state of the board
- to maximise a reward/objective: probability of winning the game
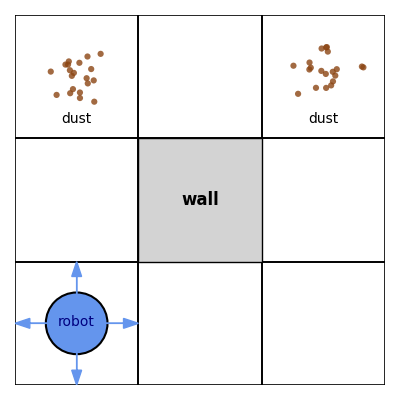
Exercise 4.2 Autonomous vacuum cleaners can be powered by reinforcement learning systems. Give examples of their:
- actions
- environment
- reward/objective
Exercise 4.3 Think of another example application of reinforcement learning.
4.1 Final Thoughts
There are three main types of Machine Learning:
- Supervised learning: generate predictions based on input/output pairs (previous chapter)
- Unsupervised learning: discover patterns and underlying structure in data
- Reinforcement learning: build models that select actions to maximise a reward while observing an environment
Machine Learning is a very exciting field. But how is this related to Artificial Intelligence and Data Science? This will be covered by the next chapter.
4.2 Solutions
Solution 4.1. Exercise 4.1
Data to collect:
- Purchase history: frequency of purchase, quantity/amount purchased
- Browsing behaviour: activity in the last month
- Demographic data: gender, age
What to do with it:
- Plot the data and observe trends or clusters
- Use clustering algorithms to identify these clusters in higher dimensions (out of this book’s scope)
Solution 4.2. Exercise 4.2
Autonomous vacuum cleaners can be powered by reinforcement learning systems. Give examples of their:
- actions: move forward/back/left/right, change power, start/stop, dock to recharge
- environment: room layout, location of dirt, battery level
- reward/objective: maximise dust collected, reduce cleaning time, avoid collisions
Solution 4.3. Exercise 4.3
Other RL example: self-driving cars
- actions: accelerate, brake, steer, signal, change lanes
- environment: road, traffic, pedestrians, weather conditions
- reward/objective: reach destination safely
Many other examples work here.